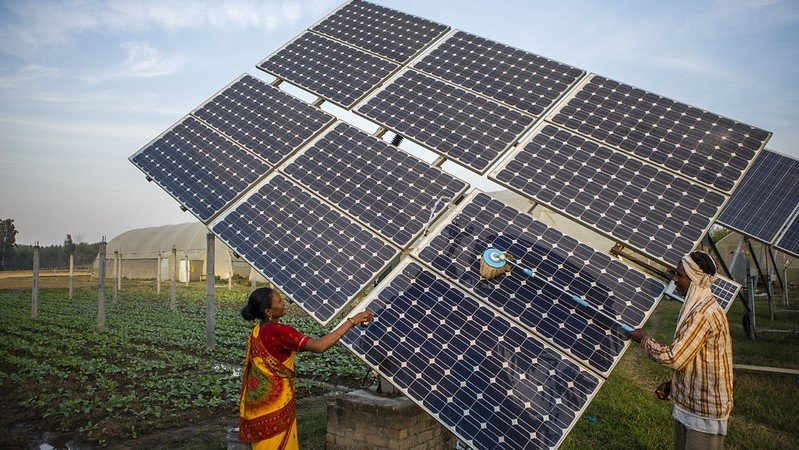
In the wake of global environmental challenges, India is making significant strides towards a greener and more sustainable future. With a burgeoning population, specifically the youth segment exceeding 480 million, and rising industrial demand, the nation’s shift from conventional fossil fuels to renewable energy sources is both a necessity and a strategic imperative. This transformation is not just about energy security or economic gains; it is a moral journey towards ensuring a healthier, equitable, and sustainable living environment for future generations.
India’s commitment to enhancing its green energy infrastructure is ambitious and visionary. The government has set a target to achieve 450 gigawatts (GW) of renewable energy capacity by 2030, up from the current 150 GW. This includes a diverse mix of solar, wind, hydro, and biomass energies, aimed at reducing the country’s carbon footprint and fostering economic resilience in the face of climate change.
Historical Shift
The journey toward renewable energy in India gained momentum in the early 2000s, with significant acceleration following the launch of the National Solar Mission in 2010. Since then, India has seen over $42 billion invested in renewable energy projects, signaling a strong shift in both policy and market dynamics towards sustainable practices. This commitment reflects a broader recognition of the need to transition away from coal and other polluting fossil fuels, which have long powered the nation’s economic engine but at a substantial environmental and health cost.
Environmental and Economic Impacts
The environmental benefits of this shift are clear. Renewable energy sources significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, crucial for a country that is the world’s third-largest emitter of carbon dioxide. Furthermore, solar and wind energy projects use far less water than traditional coal-fired power plants, helping to preserve this scarce resource for agricultural and domestic use, thus supporting India’s vast agrarian economy.
Economically, the green energy sector has become a vibrant field of opportunity. It already employs approximately 1.2 million people and is expected to create jobs for millions more as the sector expands. These opportunities are not just in urban areas; they are increasingly available in rural regions, helping to mitigate rural-urban migration and fostering inclusive economic growth.
Social and Cultural Shifts
On a social level, the spread of renewable energy has greatly improved accessibility to electricity in rural areas. This has profound implications for education, health, and economic activities, allowing children in remote areas to study after dark, families to access better healthcare, and small businesses to operate more efficiently. For the over 480 million children in India, these changes are foundational, promising a brighter and more sustainable future.
Culturally, the adoption of green energy is reshaping how communities perceive energy consumption. Sustainability is now a common theme in educational curriculums, encouraging a new generation of Indians to grow up with a strong sense of environmental stewardship. This cultural shift is crucial in sustaining long-term support for green policies and practices.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite these positive trends, the road ahead is not without challenges. India’s green transition involves complex logistical and financial hurdles, including the need for significant improvements in energy storage and grid infrastructure to manage the intermittent nature of solar and wind power. Moreover, as large-scale renewable projects require substantial land, they must be managed to avoid disrupting local ecosystems and communities.
Strategically, India needs to continue developing policies that encourage investment in green technology, remove bureaucratic obstacles, and make it easier for renewable projects to get off the ground. International partnerships and technological innovations will also play a crucial role in overcoming the remaining barriers to a fully sustainable energy network.
As India progresses on its path to a renewable future, the government’s role in shaping policies that balance economic growth with environmental sustainability will be pivotal. The focus must remain on creating an equitable energy system that benefits all segments of society, particularly the marginalized communities often hit hardest by environmental degradation.
India’s green energy revolution is a testament to its commitment to building a sustainable future. By investing in renewable resources, India is not only addressing its current environmental and economic challenges but is also laying down the foundation for a resilient and thriving future for its next generations. As the world watches, India’s energy landscape is set to be an example of how large-scale environmental challenges can be met with innovative and determined action.