In the current business environment, ESG compliance—the systematic integration of Environmental, Social, and Governance factors into organisational strategy—has evolved from a regulatory requirement into a strategic enabler. Companies that adopt comprehensive ESG frameworks enhance risk management, strengthen stakeholder relationships, and foster sustainable value creation.
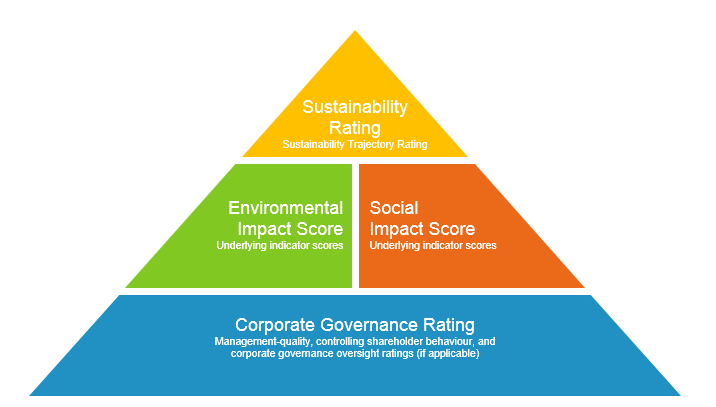
Core Components of ESG Compliance
Environmental
- Emissions Reduction: Establish definitive targets for greenhouse-gas mitigation and develop transition plans toward renewable energy sources.
- Resource Optimization: Implement initiatives to minimize water usage, reduce waste streams, and promote circular-economy practices.
- Biodiversity Preservation: Conduct impact assessments to safeguard ecosystems and natural habitats across operations and supply chains.
Social
- Inclusive Workforce: Cultivate a diverse and equitable workplace, underpinned by robust health, safety, and well-being programmes.
- Community Engagement: Forge partnerships with local stakeholders to deliver measurable benefits in education, healthcare, and livelihood development.
- Responsible Supply Chain: Enforce due-diligence protocols to ensure suppliers adhere to ethical labour standards and human-rights principles.
Governance
- Board Oversight: Integrate ESG expertise at the board level through dedicated charters, committees, and external advisors.
- Transparent Reporting: Adopt industry-recognized frameworks (e.g., GRI, SASB, TCFD) to disclose policies, performance metrics, and progress against objectives.
- Ethical Culture: Implement comprehensive codes of conduct, whistle-blower mechanisms, and regular integrity training to reinforce ethical decision-making.
Strategic Advantages of ESG Integration
- Enhanced Risk Management
Embedding ESG in enterprise-risk frameworks uncovers latent liabilities—ranging from regulatory changes to reputational vulnerabilities—and facilitates proactive mitigation measures. - Improved Capital Access
Financial institutions and investors increasingly incorporate ESG criteria into their underwriting and investment decisions. Demonstrable ESG performance can result in more favorable financing terms and broadened access to sustainability-linked funding. - Operational Efficiencies
Initiatives such as energy-efficiency retrofits, waste-stream optimization, and compliance automation yield direct cost reductions and bolster operational resilience against resource volatility. - Talent Acquisition and Retention
A credible ESG commitment enhances employer value proposition, particularly among Millennial and Gen-Z cohorts who prioritize purpose and corporate citizenship alongside remuneration. - Reputation and Brand Equity
Consistent, data-driven ESG disclosures build stakeholder confidence—strengthening brand loyalty, differentiating market positioning, and providing insulation against public-relations risks.
Implementation Framework
- Executive Sponsorship
Secure unequivocal endorsement from the C-suite and board. Allocate dedicated resources and define clear accountability structures to drive ESG objectives. - Cross-Functional Integration
Establish ESG working groups that bring together sustainability, operations, finance, legal, and human-resources functions to ensure cohesive execution and knowledge sharing. - Defined Roadmaps and KPIs
Develop phased implementation plans with quantifiable milestones (e.g., percentage reduction in carbon intensity, workforce-diversity targets, supplier-audit coverage) and assign ownership to specific leaders. - Digital Enablement
Deploy data-management platforms and analytics tools for real-time tracking of environmental footprints, social metrics, and governance processes, enabling agile responses and continuous improvement. - Stakeholder Engagement and Disclosure
Maintain open dialogue with investors, regulators, employees, customers, and community representatives. Leverage their feedback to refine strategies and enhance transparency in public reporting.
Monitoring and Reporting
A robust ESG programme combines quantitative metrics with qualitative insights to convey a holistic narrative of performance:
- Quantitative: Emissions-reduction figures, diversity ratios, compliance-audit completion rates.
- Qualitative: Case studies on community-impact projects, employee-engagement surveys, board-governance summaries.
- Integrated Reporting: Present ESG and financial outcomes in a unified report, demonstrating the linkage between sustainability initiatives and business results.
Illustrative Case Study: Mid-Market Manufacturer
A mid-sized manufacturing enterprise confronted escalating energy costs and local concerns regarding air emissions. Taking a comprehensive approach, the company:
- Partnered with an academic research centre to implement a waste-heat recovery system.
- Established vocational training for community members in sustainable manufacturing techniques.
- Revised its board governance structure to include two non-executive directors with ESG specialization.
Within eighteen months, the organisation achieved a 15% reduction in energy expenditures, garnered positive community sentiment, and secured a sustainability-focused investment. This example highlights how strategic ESG adherence can drive both financial performance and social licence to operate.
The Path Forward
As regulatory requirements tighten, investor scrutiny intensifies, and societal expectations evolve, organisations that embed ESG into their strategic DNA will realize competitive advantage and resilience. By approaching ESG compliance as an ongoing strategic discipline—rather than a transactional obligation—companies can cultivate stakeholder trust, drive operational excellence, and deliver sustainable growth.
At Gentle and wise Global Consulting, we partner with you to design and execute an ESG roadmap that aligns with your strategic objectives, operational capabilities, and stakeholder aspirations—ensuring that every business decision contributes to lasting value and responsible stewardship.